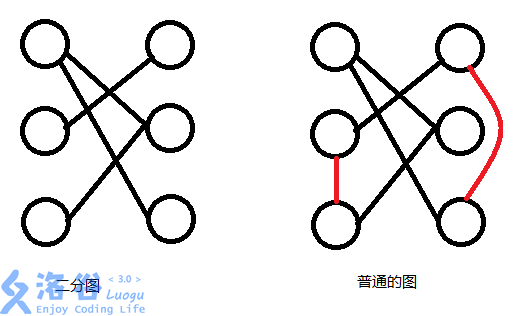
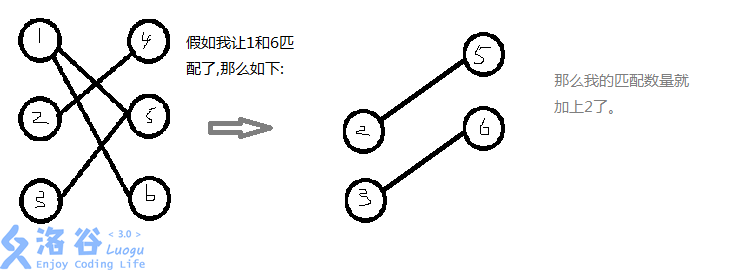
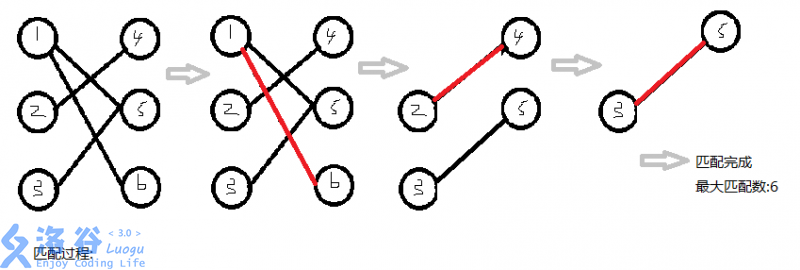
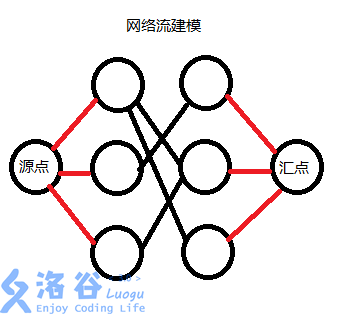
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
| //可能因为pascal或者是初始化的原因,有些时候被Dinic赶超,不过时间复杂度还是很乐观的。(可以开O2)
//少了建模和添边,ISAP的DFS只占很少Byte。
//以下程序只是介绍建模部分
Uses math;
var
value,reach:array[0..2010] of longint;
dis,gap,cnt,next:array[1..1010] of longint;
n,m,source,sink,tot,x,y,sum,i,k:longint;
maxflow:int64;
procedure add(x,y,sum:longint);
begin
inc(tot);
reach[tot]:=y;
inc(value[tot],sum);
next[tot]:=cnt[x];
cnt[x]:=tot;
end;
function Dfs(now,flow:longint):longint;
var
i,k,mindis,ret:longint;
begin
mindis:=n-1;
ret:=flow;
if now=sink then
exit(flow);
i:=cnt[now];
repeat
if value[i]>0 then
begin
if dis[now]=dis[reach[i]]+1 then
begin
k:=Dfs(reach[i],min(ret,value[i]));
dec(value[i],k);
inc(value[i xor 1],k);
dec(ret,k);
if dis[source]>=n then
exit(flow-ret);
if ret=0 then
break;
end;
mindis:=min(mindis,dis[reach[i]]);
end;
i:=next[i];
until i=-1;
if ret=flow then
begin
dec(gap[dis[now]]);
if gap[dis[now]]=0 then
dis[source]:=n;
dis[now]:=mindis+1;
inc(gap[dis[now]]);
end;
exit(flow-ret);
end;
begin
filldword(cnt,sizeof(cnt) div 4,maxlongint*2+1);
tot:=1;
read(n,m,k);
source:=1;
sink:=n+m+2;
for i:=1 to n do //源点向左边的点添边
begin
add(source,i+1,1);
add(i+1,source,0); //注意:反向边依然是0
end;
for i:=1 to k do //创建二分图
begin
read(x,y);
if (x>n)or(y>m) then //Bug
continue;
add(x+1,y+n+1,1);
add(y+n+1,x+1,0);
end;
for i:=1 to m do //右边的点向汇点添边
begin
add(i+n+1,sink,1);
add(sink,i+n+1,0);
end;
n:=n+m+2;
gap[source]:=n; //ISAP网络流部分
while dis[source]<n do
inc(maxflow,Dfs(source,maxlongint));
writeln(maxflow);
end.
|